PPE for the sanitation sector
The water and wastewater treatment professions are subject to numerous risks, particularly chemical and biological. Body protection must be adapted to the substances present in wastewater and necessary for water treatment. Workers also have to deal with the risk of splashing liquids from leaking pipes.
The main risks associated with wastewater treatment jobs
The most common hazards include contact with biological pathogens (bacteria, viruses, parasites), exposure to toxic substances, the release of noxious gases (such as hydrogen sulphide), as well as physical risks such as slips, falls or injuries from using heavy equipment.
To guarantee their safety and prevent contamination, professionals must have appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Chemicals carried by wastewater and water treatment
Wastewater contains a variety of chemicals, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, pesticides and drug residues, which can be toxic, corrosive or carcinogenic. These substances expose workers to risks of poisoning, irritation or chronic effects.
To limit these dangers, companies must comply with strict standards, in particular those set out in the French Environment Code and the European Water Framework Directive, which require the monitoring of discharges and appropriate treatment.
Biological agents in wastewater
Wastewater is teeming with biological agents such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites, which can cause serious infections or respiratory, skin and gastrointestinal diseases in exposed workers. The risk of contamination is particularly high during maintenance or direct treatment operations.
To prevent these dangers, companies must comply with existing health standards, such as those defined by the French Labour Code and WHO recommendations, by ensuring rigorous management of biological risks. Wearing PPE (gloves, masks, overalls) and regular training are essential to protect workers effectively.
What are the high-risk jobs in the wastewater treatment sector?
Sanitation workers
Sanitation workers are exposed to the risk of biological infections from pathogens in wastewater, burns from cleaning products, and physical injuries from falls or handling heavy equipment in unsanitary environments.
Sewage worker
Sewage workers face risks of exposure to biological agents, injuries from heavy or high-pressure equipment, and accidents in confined spaces, such as falls or respiratory problems due to poor air quality.
Sanitation drivers
Sanitation drivers are exposed to the physical risks associated with high pressure, injuries from contact with toxic substances and traffic accidents, whether in the field or during pumping and cleaning.
What are the high-risk jobs in wastewater treatment?
Water quality officer
Water quality agents are exposed to risks associated with treatment products, as well as biological risks due to contact with potentially contaminated wastewater and sludge. Working on heavy equipment also presents mechanical hazards, such as injuries or accidents during repairs and troubleshooting.
Water treatment equipment operator
Equipment operators share the same chemical risks, particularly when handling treatment products, as well as biological risks linked to exposure to wastewater. There are also mechanical risks when checking and working on valves, pumps and filters.
Drinking water treatment technician
Technicians face risks associated with the preparation and handling of treatment reagents, biological risks from water and pathogens, and mechanical hazards during equipment maintenance and repair operations.
What PPE should you choose to protect yourself against the risks associated with wastewater treatment?
The choice of PPE must take into account the risks, working conditions (humidity, heat, confined spaces) and regulations in force. Effective selection is based on an assessment of the hazards specific to each task, ensuring that the PPE complies with safety standards and is comfortable for prolonged use.
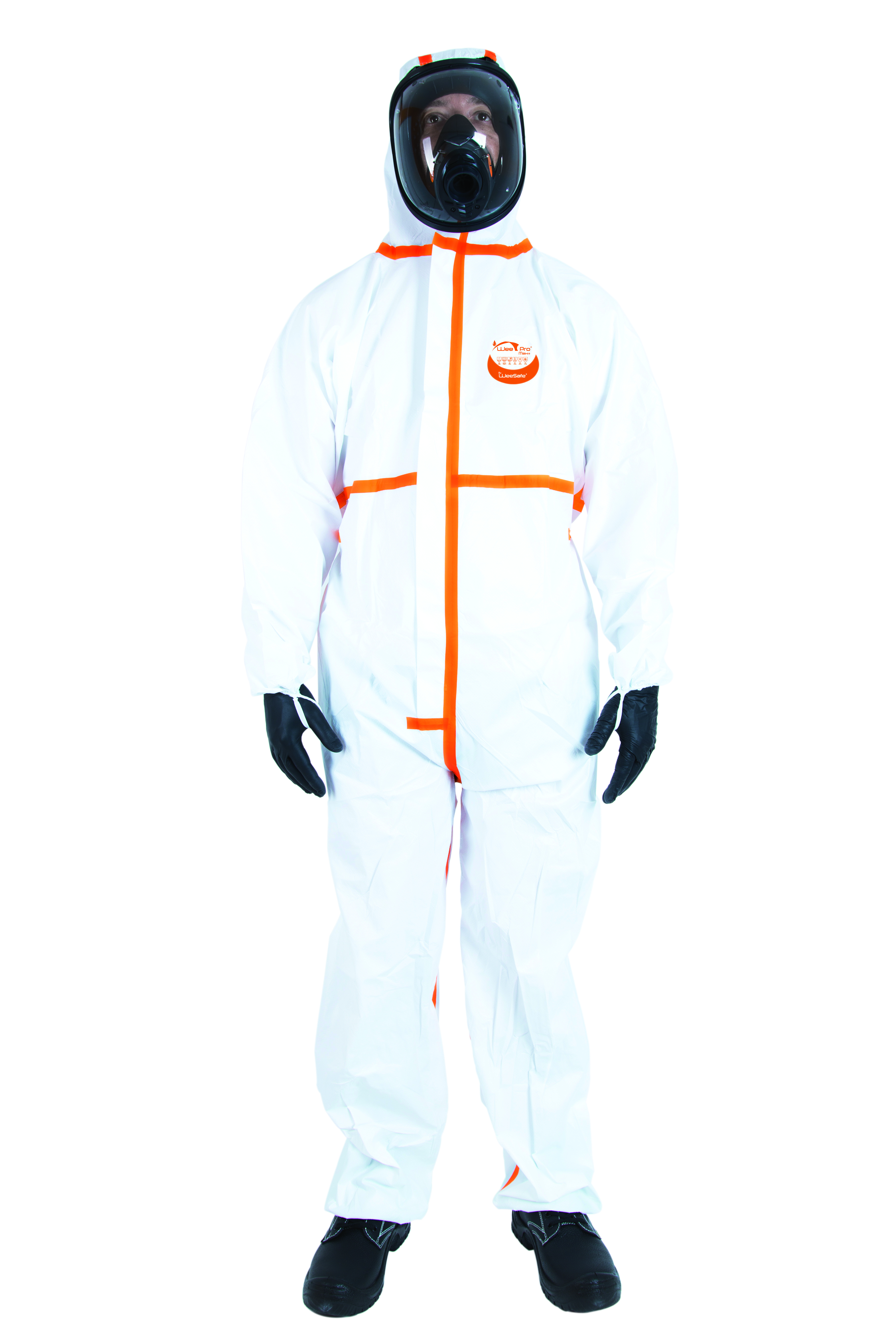
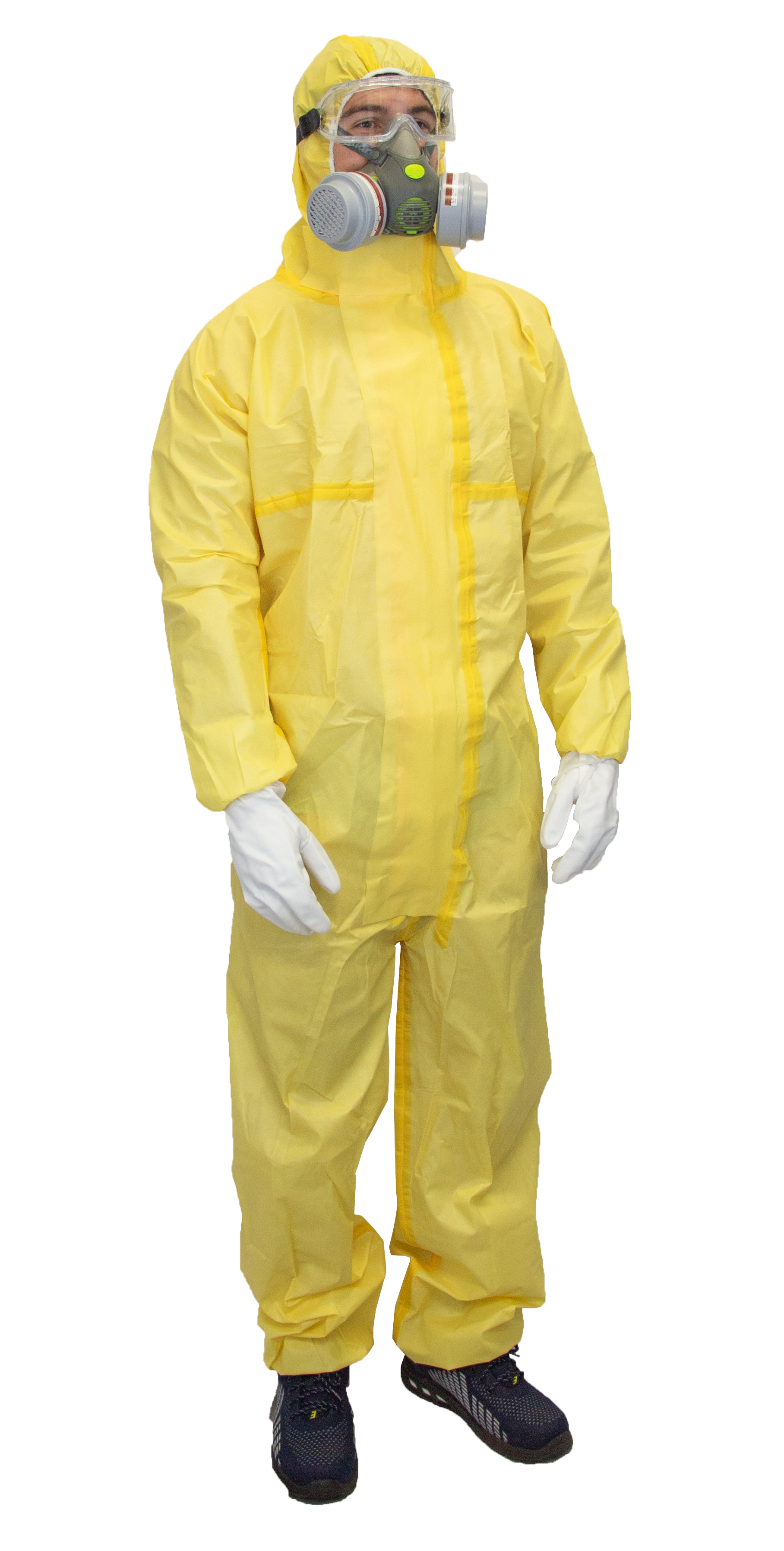
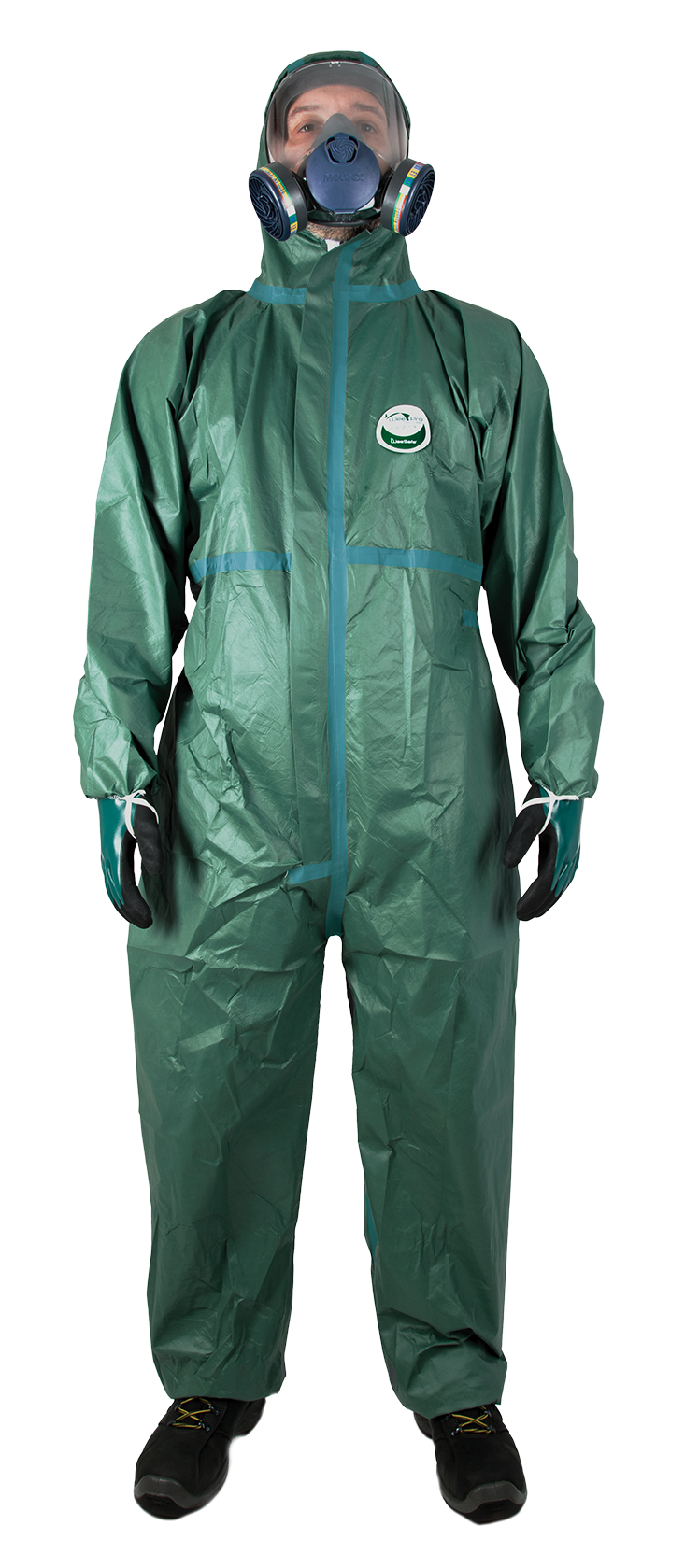
Coveralls
Coveralls protect the whole body against pathogens, chemical substances and splashes of contaminated liquids. They are an essential barrier to limit direct contact with dangerous elements in the environment.
Gloves
Gloves provide essential protection against cuts, irritations or chemical burns when handling waste, corrosive products or tools. They must be strong and suitable for the substances being handled.
Respiratory protection masks
Masks filter out fine particles, micro-organisms, toxic gases and unpleasant odours. They are crucial for protecting the respiratory tract in confined spaces or in the presence of noxious fumes and vapours.
Protective eyewear
Goggles protect the eyes from splashes, flying particles or irritants. They are essential for avoiding contact with contaminated or corrosive substances.
Safety shoes
Reinforced footwear prevents slipping, punctures or crushing in wet and uneven environments. They provide stability and foot protection in sometimes unstable work areas.
Helmets
Helmets protect the head from falling objects or impacts in confined spaces or at height. They are essential for reducing the risks associated with unforeseeable accidents.
All equipment must be properly maintained and replaced as soon as it shows signs of wear or failure, to ensure optimum protection.
How should PPE be maintained?
Following good PPE maintenance practices ensures worker safety, complies with health regulations and reduces costs.
Storage
Store PPE in its original packaging, away from moisture, heat and chemicals, to prevent deterioration before use.
Handling
Put them on with clean hands to avoid contamination and make sure they fit properly before working.
Single use
Never re-use this equipment, even if it appears to be intact, as its effectiveness diminishes after initial use.
Disposal
Dispose of in a container suitable for contaminated or hazardous waste to avoid any risk of spreading or contamination.
Setting up a living base
Set up as part of the wastewater treatment and purification process, a base camp guarantees the safety and protection of workers. It centralises the collection and storage of PPE and the disinfection process.
It provides workers with access to the equipment they need to protect themselves against biological and chemical risks (pathogens, toxic substances) and offers a dedicated area for hygiene and waste management, promoting a safe working environment that complies with health standards.
Medical monitoring
Strict medical supervision is essential for employees working in the wastewater and sewage treatment sector, because of the high health risks involved. Exposure to pathogens, chemicals or unhealthy conditions can seriously affect their health.
This regular monitoring makes it possible to detect contamination or occupational illnesses at an early stage, to ensure compliance with health and safety standards in the workplace, and to adjust prevention measures according to the risks.