PPE for shipyards
Work in nautical maintenance and construction involves the use of numerous chemicals, such as solvents, paints, gelcoats, antifouling agents, and resins. These substances are commonly used in tasks such as stripping, painting, and sanding hulls during renovations.
These activities expose operators to multiple risks, particularly intense dust generated during processes such as molding. These particles can be harmful to their health, as can vapor emissions and chemical splashes.
To assess risks, it is crucial to carefully analyze the form of the chemical. Is it solid or liquid? If liquid, how can it reach the operator? The risks vary depending on whether the product is a small splash, a large spray, or an aerosol.
Finally, knowing the exact composition of the chemical is essential for choosing the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring worker safety.
PPE: protective clothing on shipyards
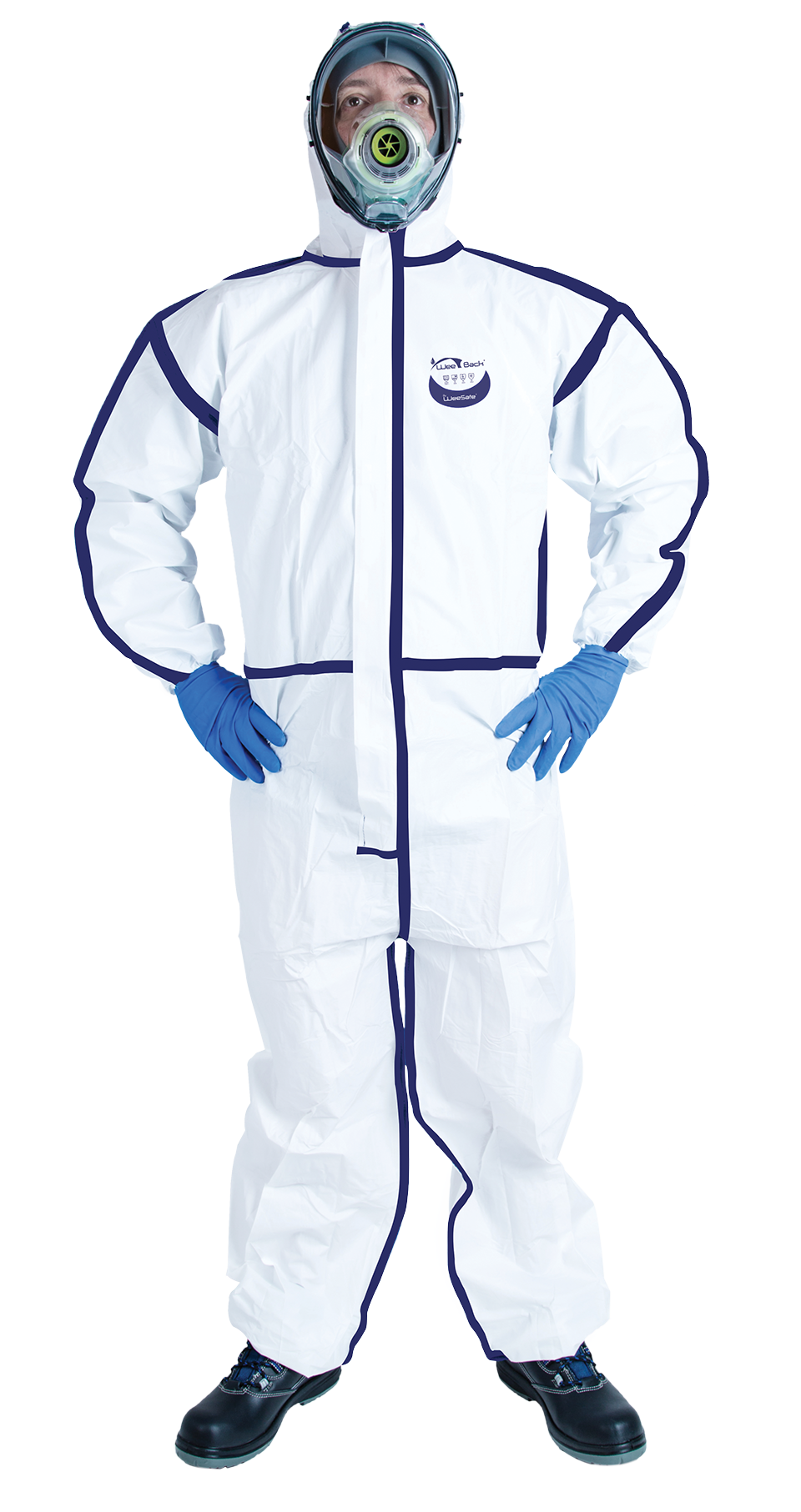
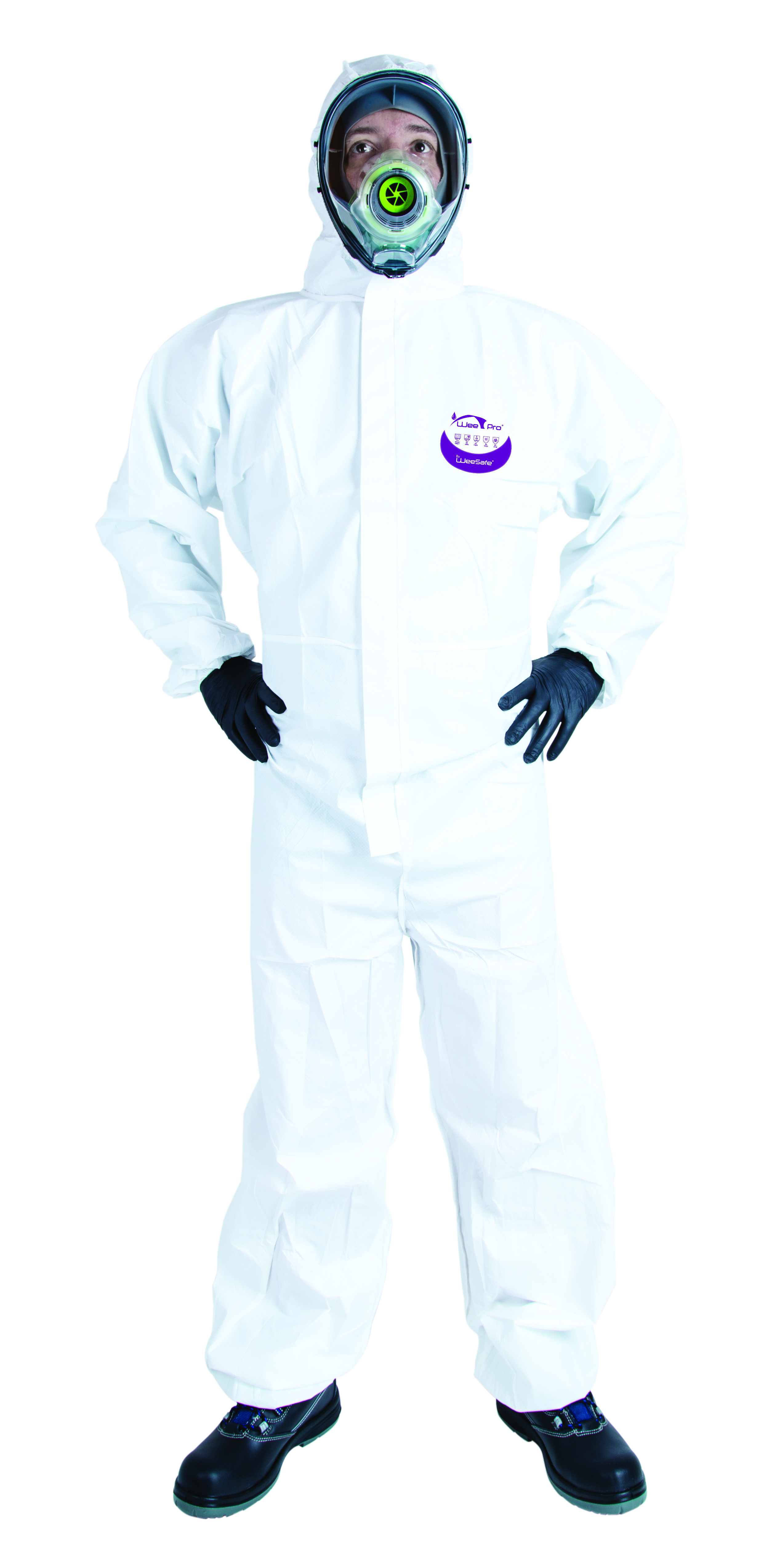
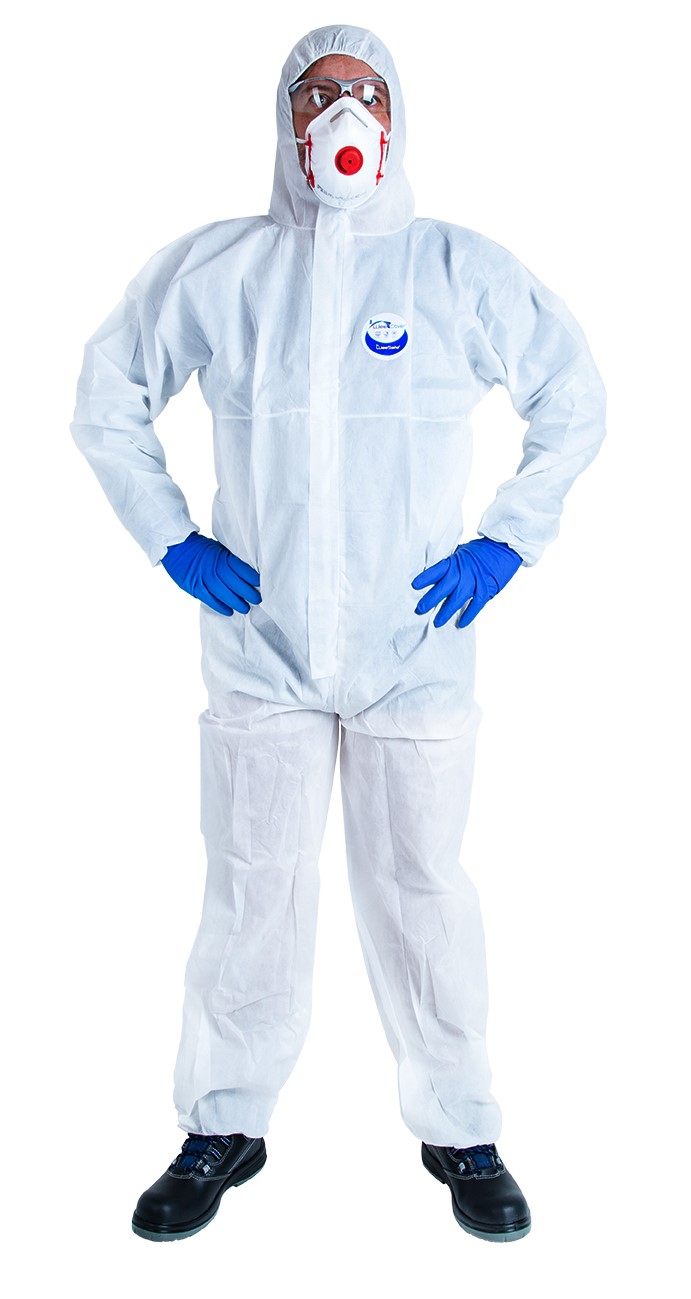
In the marine industry, operators handle chemicals and are exposed to hazardous dust. Protective suits are essential for preventing irritation, allergies, and poisoning by creating an effective barrier against splashes and particles.
In addition to protecting against chemical and biological risks, they contribute to user comfort, essential during long workdays. Choosing the right suit ensures safety and efficiency in the demanding environments of this sector.
Coveralls
What risks are workers exposed to on a shipyard?
Shipyard workers face numerous risks related to handling chemicals and performing mechanical operations. These activities expose them to toxic fumes, chemical splashes, and fine dust.
Wearing PPE such as waterproof suits, respirators, heavy-duty gloves, and safety goggles is essential to maintain their health and ensure their daily safety.
Boat maintenance
| Sanding | Chemical stripping | Sandblasting |
|---|---|---|
| Wood, plastic, or fiberglass dust projections can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation. These fine particles, when inhaled, pose long-term risks to the respiratory tract. | The use of stripping solvents (such as methylene chloride) or alkaline and acidic products (soda, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid) can cause serious chemical burns and respiratory irritation in the event of fumes or splashes. | Solid residues (rust, paint, glue, varnish) generated during this operation can cause mechanical injuries or prolonged exposure to toxic substances. |
| Maintenance and cleaning operations | Shell treatments | Antifouling |
|---|---|---|
| Detergents, disinfectants and other cleaning products used present risks of contact with the skin, which can cause irritation or allergic reactions. | Organic resins and solvents (styrene, methyl methacrylate) are highly toxic and emit dangerous fumes. These substances can cause neurological or respiratory problems. | The biocides contained in these products pose risks of acute toxicity to operators in the event of direct contact or inhalation. |
Boat building
| Machining and sanding of materials | Gun casting | Sandblasting |
|---|---|---|
|
Wood, plastic, lead, and fiberglass dust thrown up during these operations can cause respiratory, skin, and eye irritation. In the long term, inhaled particles increase the risk of chronic respiratory diseases. |
Resins applied at low or medium pressure emit styrene vapors, a compound toxic to the central nervous system, which can also cause headaches and respiratory irritation. |
The use of solvent-based paints releases aerosols containing dangerous volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can be inhaled or come into contact with the skin. |
| Hand casting | Preparation of the mixtures | Cleaning tools |
|---|---|---|
|
Direct application of resins results in increased exposure to styrene, both in liquid and vapor form, requiring specific protection to limit direct contact and inhalation. |
Handling cobalt resins, catalysts and salts involves risks of corrosive chemical splashes that can cause burns or irritation. |
The use of solvents such as acetone exposes operators to risks of skin contact and inhalation, leading to irritation or poisoning in the event of poor ventilation. |
These activities require compliance with strict standards, such as EN 14605 for protective clothing against liquid splashes and EN 374 for chemical-resistant gloves.
What PPE is suitable for working on a shipyard?
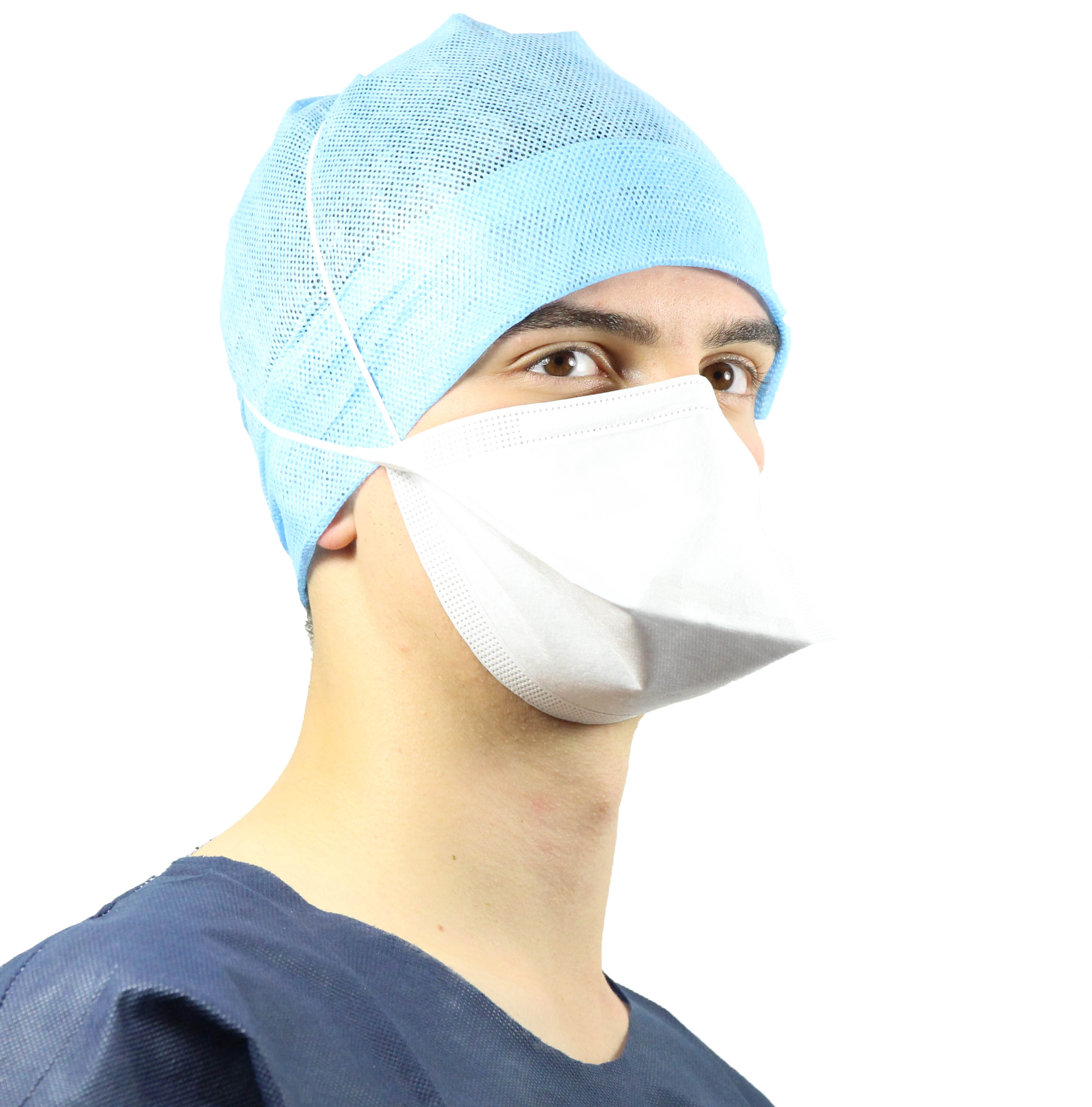
Respiratory protection masks
Les masques de protection respiratoire sont indispensables pour protéger les voies respiratoires des travailleurs exposés aux émanations de solvants, résines et particules fines. Ces masques filtrent efficacement les aérosols et composés organiques volatils (COV), réduisant les risques de maladies respiratoires et d’intoxications dues à l'inhalation de produits chimiques.
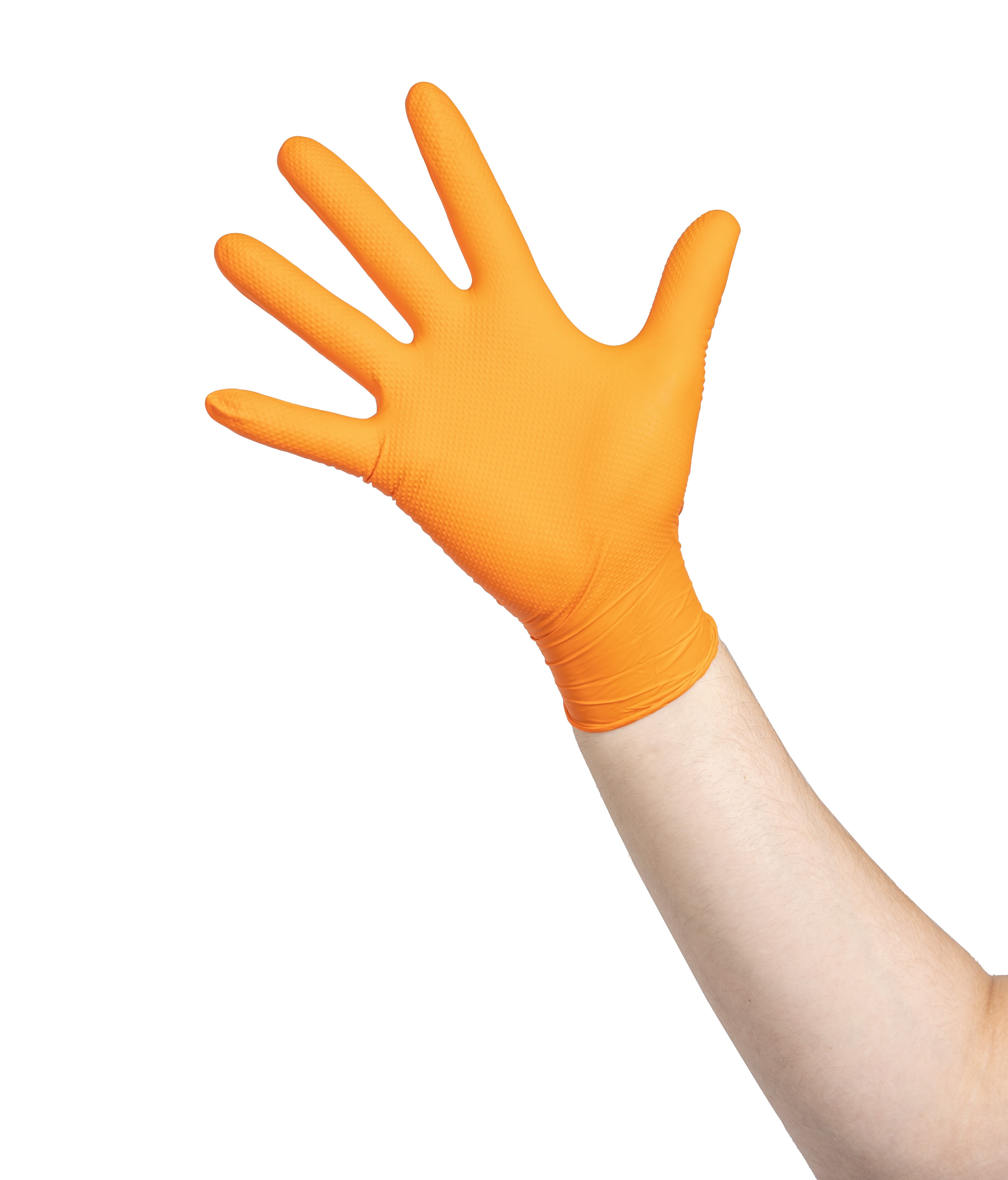
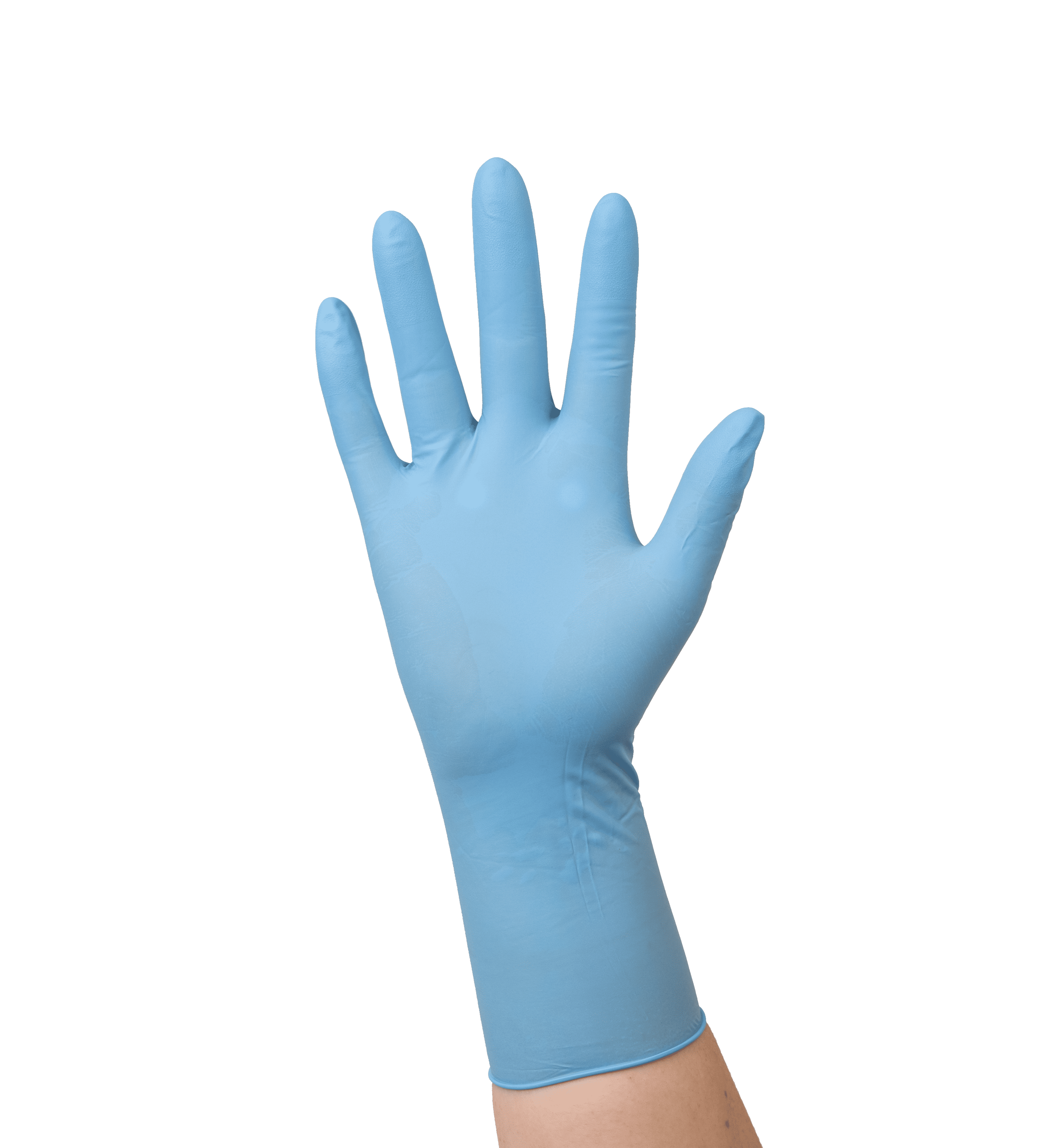
Gloves
Safety gloves, such as nitrile or butyl gloves, are crucial for protecting workers' hands from chemical hazards associated with resins, solvents, and products used in maintenance and construction. They provide resistance to chemical splashes and protection against irritation or burns, while allowing for precise handling of tools and materials.
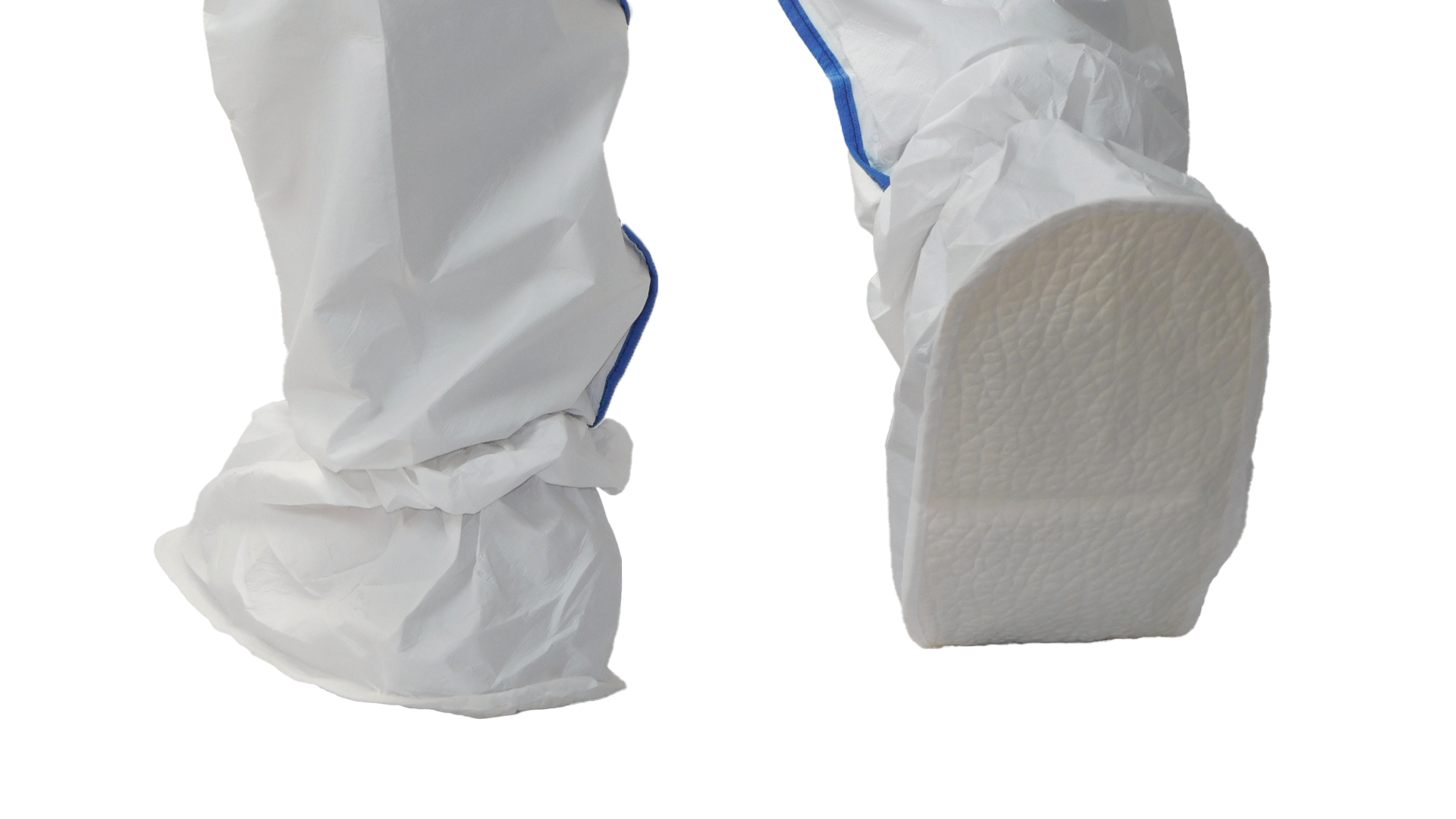
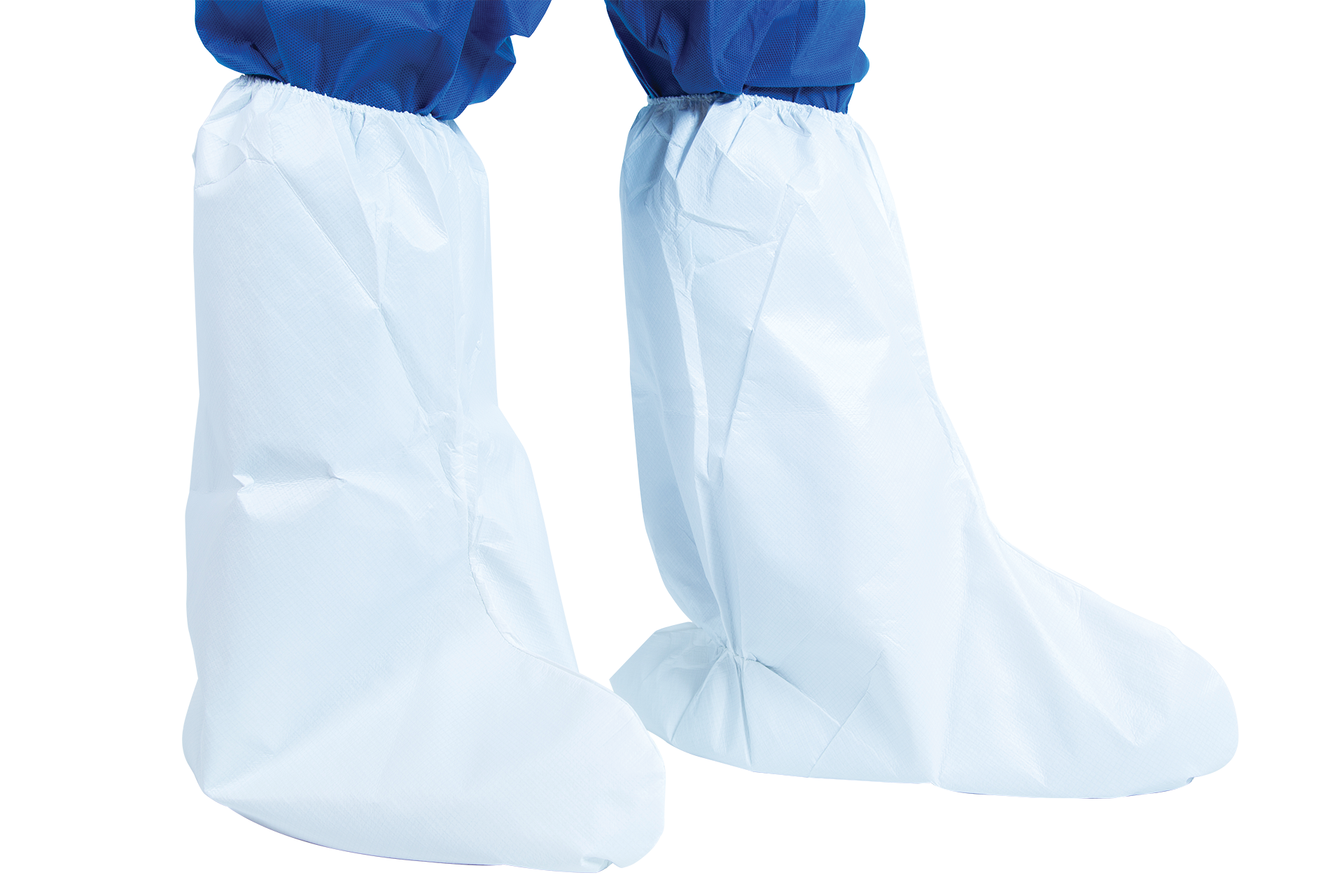
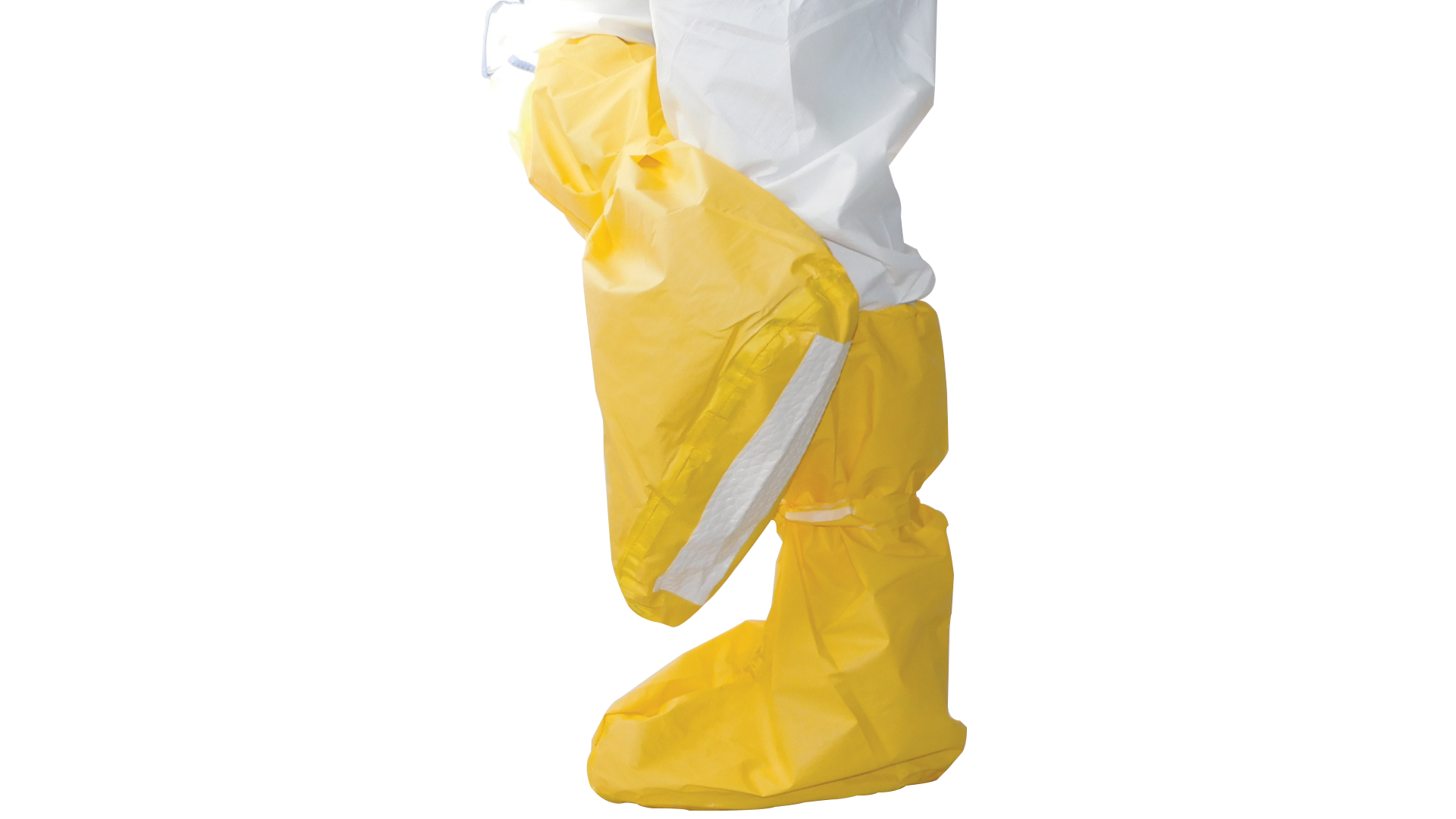
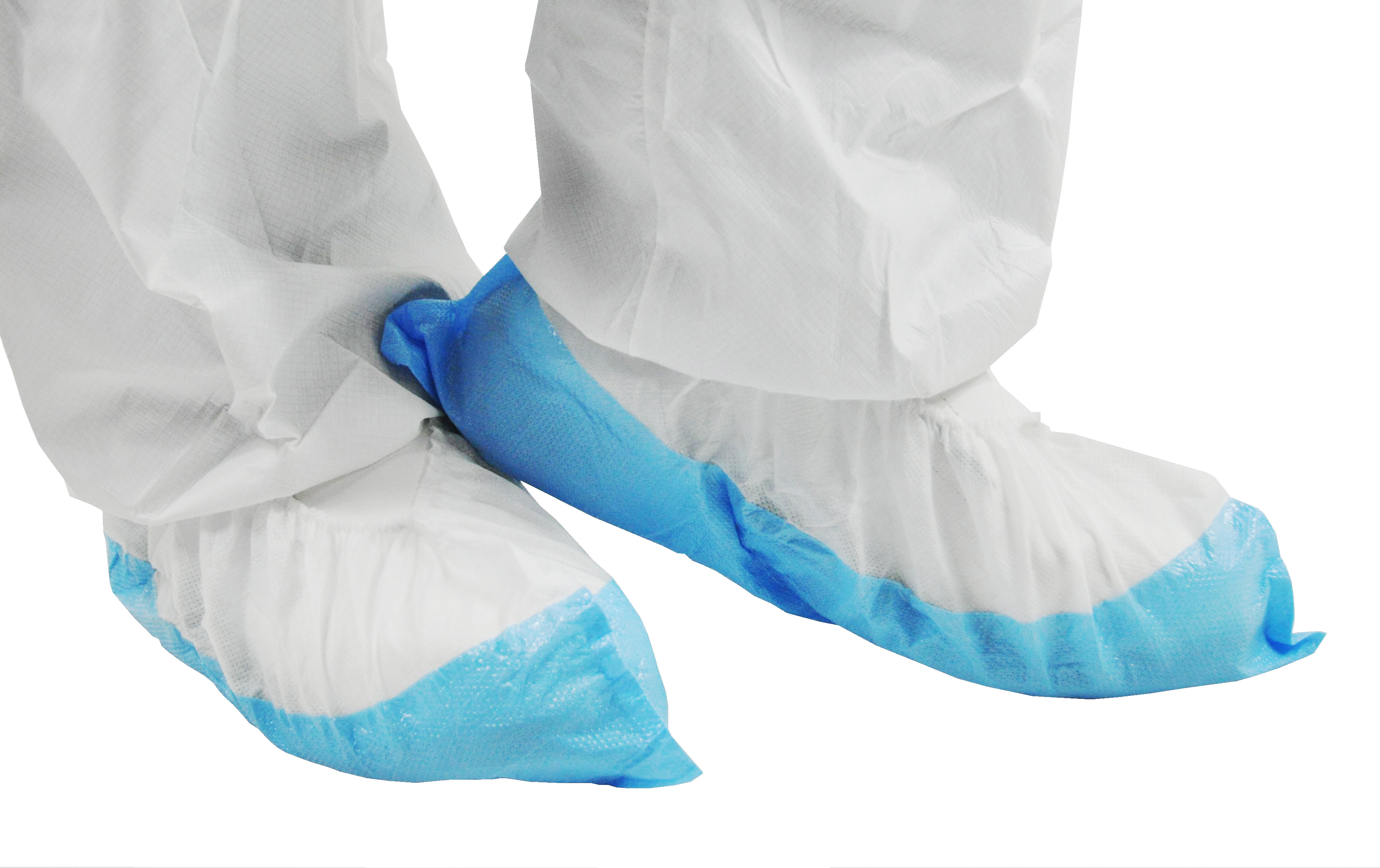
Shoecovers and overboots
Chemical-resistant overshoes and boots provide foot protection against splashes of paints, solvents, and other products. They also protect against falls and exposure to corrosive substances, while also providing protection against moisture and harsh working conditions.
Goggles
Safety goggles or face shields are essential for protecting eyes from chemical splashes, fine dust, and particles. They are particularly useful when sanding, spraying paint, or applying resins. Anti-fog models ensure optimal visibility, even in hot and humid environments.