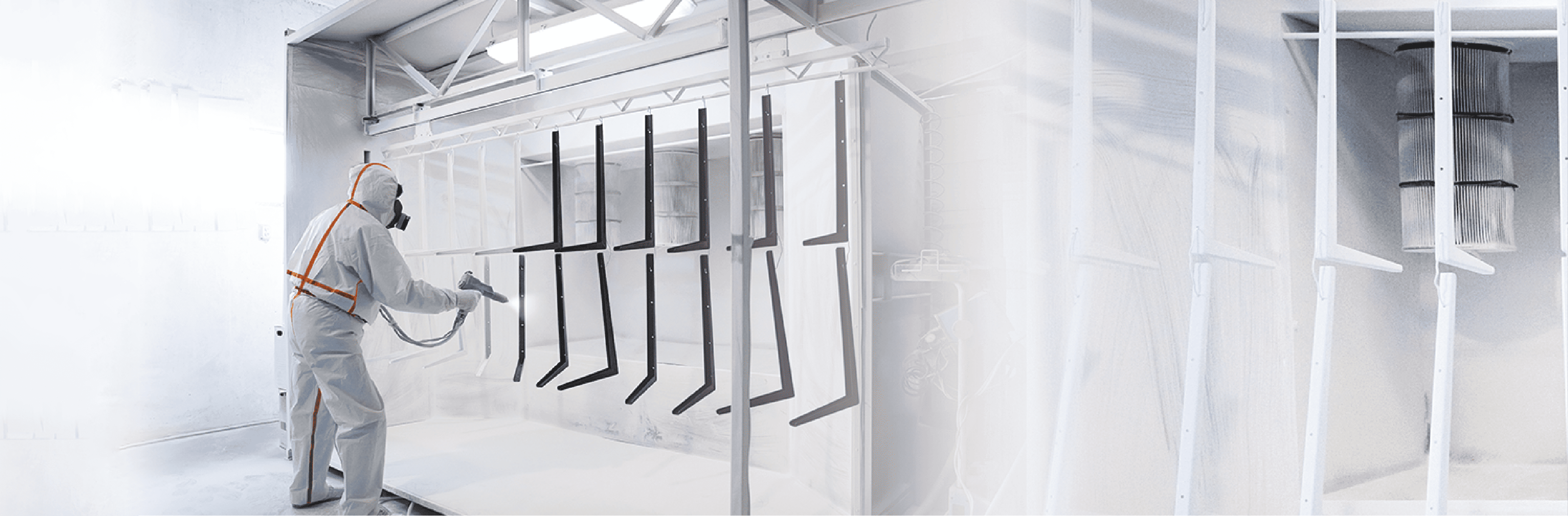
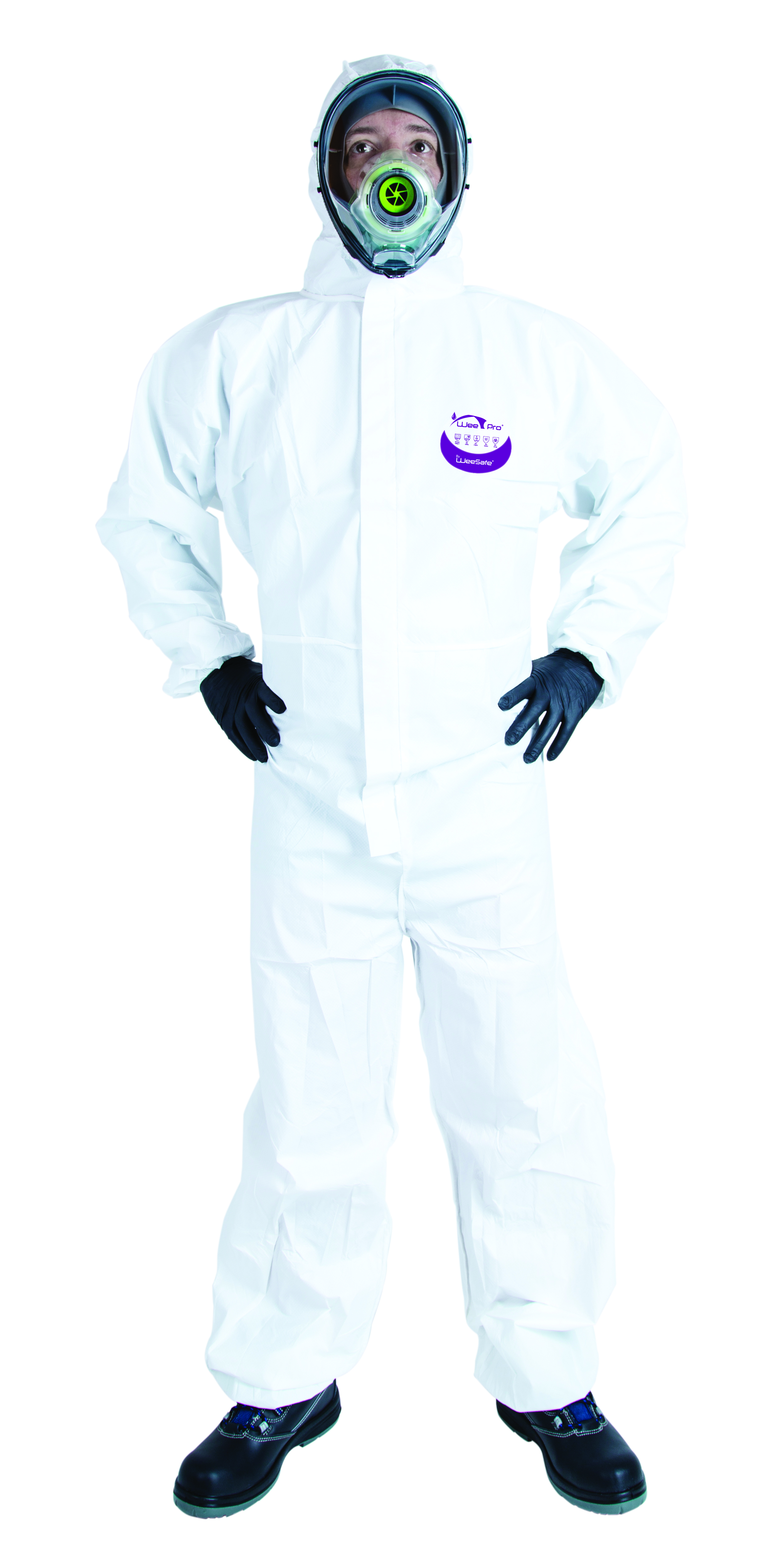
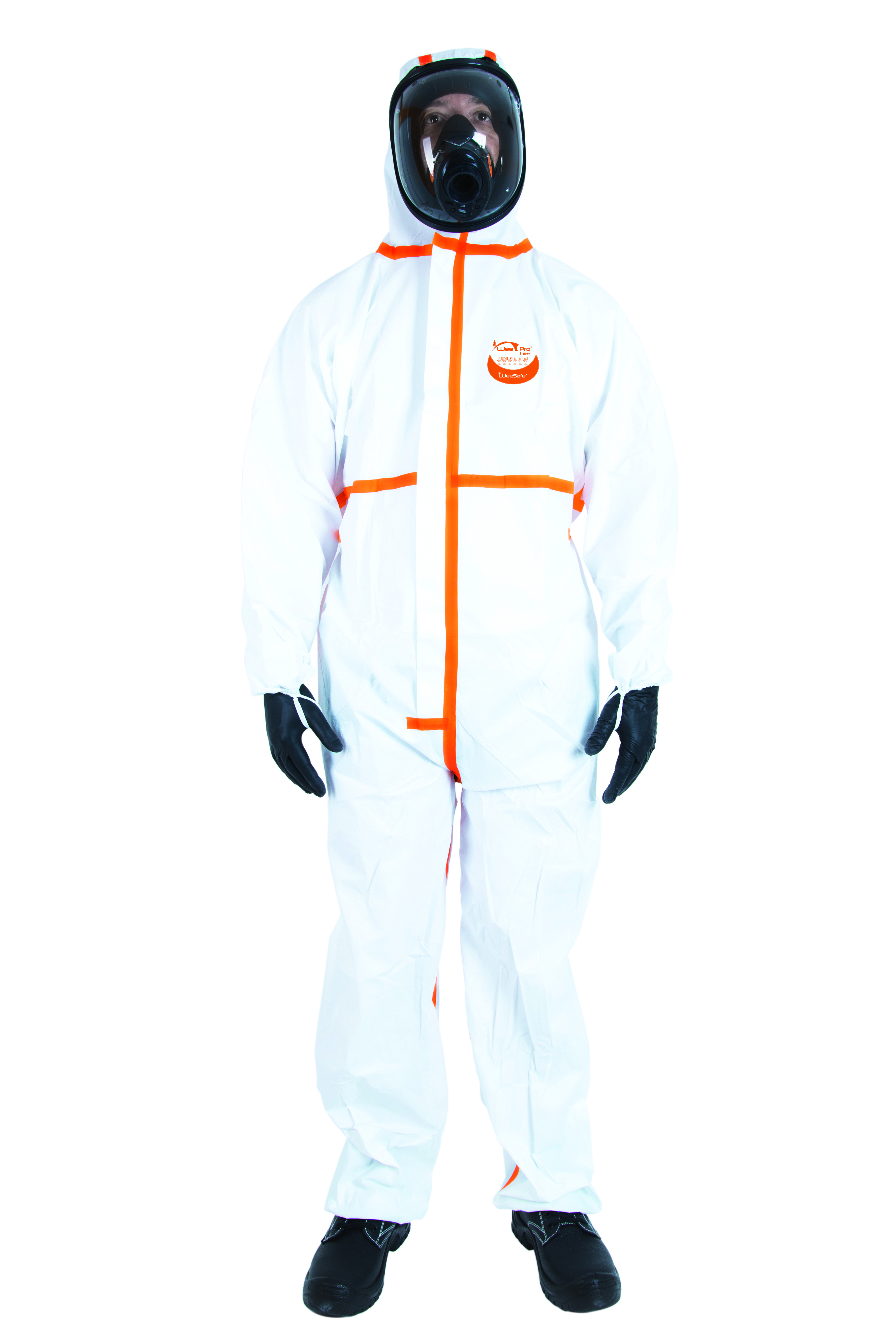
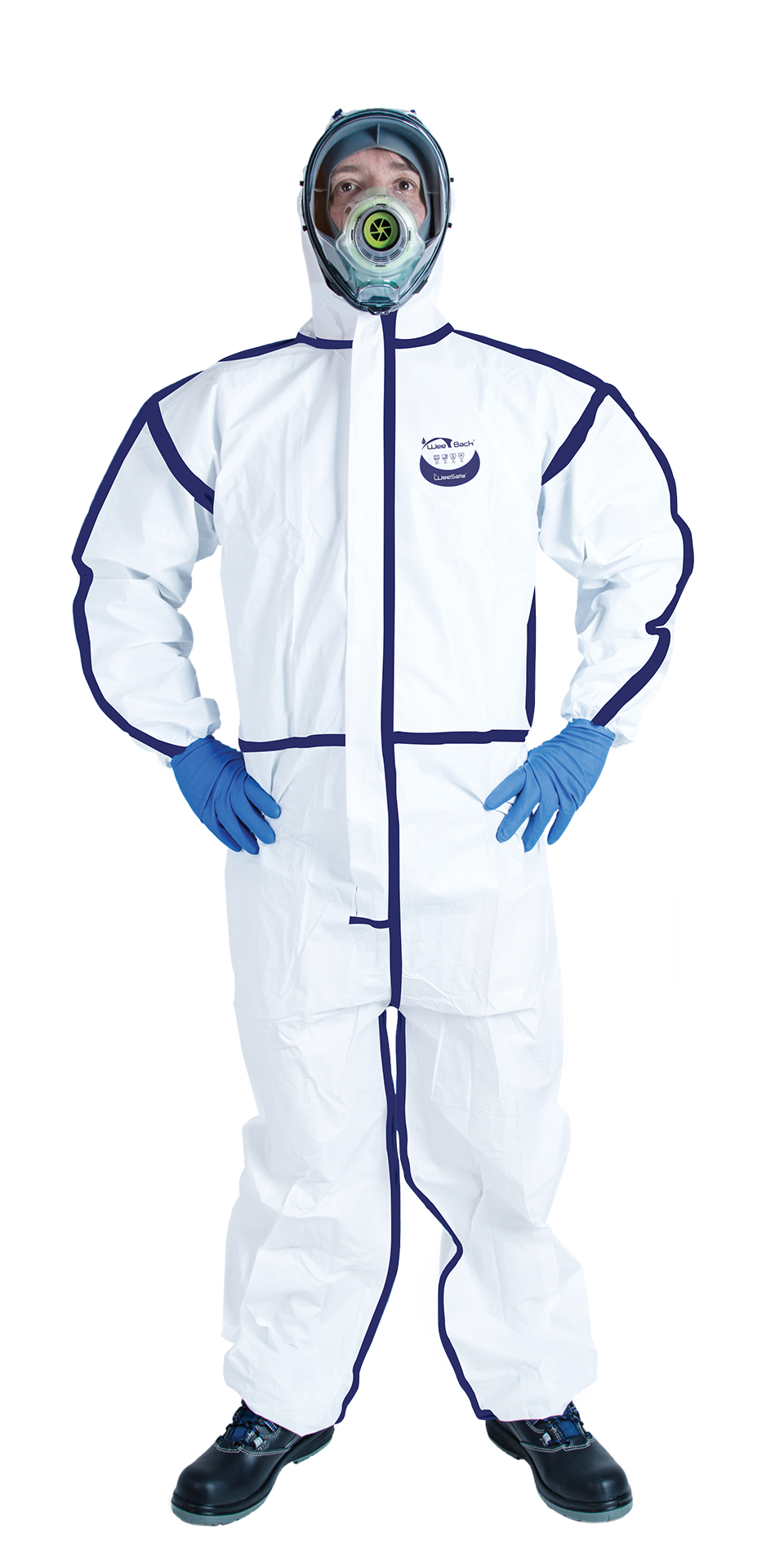
What personal protective equipment should I choose?
In the paint industry, 3 main categories of paint are used: waterborne paint, powder paint and solvent-based paint (the most hazardous to health, widely used in industrial environments). Our protective solutions offer seams that are impervious to liquid aerosols and powder splashes, providing optimum protection for workers.
Our protective solutions offer seams that are impervious to liquid aerosols and powder splashes, ensuring optimum protection for workers. By choosing our coveralls, workers considerably reduce their exposure to these hazards and guarantee their safety at work.
The main risks associated with painting
It is essential to protect against the health hazards associated with exposure to the chemicals contained in paints. The vapours and particles emitted during application can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation and other adverse health effects.
Waterborne paint
![]() Risks:
Risks:
- Inhalation of vapours and aerosols: may cause respiratory tract irritation, coughing, headaches and dizziness.
- Skin contact: may cause skin irritation, dermatitis and allergic reactions.
- Eye contact: may cause eye irritation and redness.
Exposed occupations:
- House painters
- Car industry workers
- Furniture manufacturers
Powder paint
![]() Risks:
Risks:
- Inhalation of fine particles: may cause respiratory problems, such as asthma, respiratory tract irritation and chronic lung disease.
- Skin contact: may cause skin irritation and allergic reactions.
- Risk of explosion: powder paint dust can form explosive atmospheres if suspended in air and in contact with a source of ignition.
Exposed occupations:
- Powder coating line operators
- Workers in the metal industry
- Manufacturers of household appliances
Solvent-based paint
![]() Risks:
Risks:
- Inhalation of vapours: May cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, neurological disorders and long-term damage to the central nervous system.
- Skin contact: May cause skin irritation, dermatitis and allergic reactions.
- Eye contact: May cause eye irritation and damage.
- Fire and explosion hazards: Solvents are highly flammable and may create explosion hazards. Friction, contact or separation generate static electricity which, if not dissipated by appropriate earthing, can discharge spontaneously creating a high voltage spark.
Exposed occupations:
- Industrial painters
- Marine industry workers
- Manufacturers of electronic products
Our PPE to protect you from the risks of painting
For each of these types of painting, it is essential to wear suitable personal protective equipment (PPE) such as protective overalls, full-face or cartridge respirators, gloves, overshoes, etc.
Coveralls
Protective suits are essential for painters to protect themselves effectively against paint splashes and chemical substances. Our coveralls are available in a range of sizes and provide a complete barrier for maximum safety on the job.
Gloves
Gloves are essential equipment for ensuring the safety and protection of painters during their work. Available in different sizes and materials, our gloves offer optimum protection against chemicals, abrasives and other hazards associated with painting.
Shoecovers
Overshoes are crucial to ensuring protection and maintaining cleanliness on the worksite when painting. Our high-quality overshoes, available in a range of sizes, protect your shoes from splashes while ensuring perfect grip on the ground.
How to choose PPE for industrial painters?
It is crucial to select the right protective suit for working with paint, taking into account the quantity of paint used, the application method and ventilation conditions.PPE is classified into three categories according to their level of protection.
PPE categories
Category I: Simple protection
- Description : PPE of simple design designed to protect against minimal risks.
- Examples : light gloves, dust masks.
- Use : light painting tasks where the threats are low, such as water-based paint in a well-ventilated environment.
Category II: Intermediate protection
- Description : PPE designed to protect against intermediate risks. They must be certified by a notified body.
- Examples : chemical-resistant gloves, breathing masks with interchangeable filters.
- Use : moderate painting tasks where the threats include skin irritation and inhalation of chemical vapours, such as powder paint.
Category III: Complex protection
- Description: PPE of complex design designed to protect against serious risks. They require rigorous quality control and certification by a notified body.
- Examples : drysuits, self-contained breathing apparatus, anti-cut and anti-chemical gloves.
- Use : high-risk painting tasks, such as solvent-based painting in confined spaces, where there is a high risk of inhalation of toxic fumes and explosion.
Criteria for choosing PPE
Compliance with standards
Check that PPE complies with European standards (CE marking) and has been certified by a notified body. Make sure that Category II and III PPE has instructions for use and a certificate of conformity.
Adapting to the risk
Assess the risks specific to your working environment (inhalation of vapours, contact with chemical substances, explosion) so that you can choose PPE that offers adequate protection against them.
Comfort and ergonomics
Opt for PPE that is comfortable to wear for long periods - a good fit is crucial to ensure effectiveness and comfort. Look for lightweight, well-ventilated equipment to minimise fatigue and improve productivity.