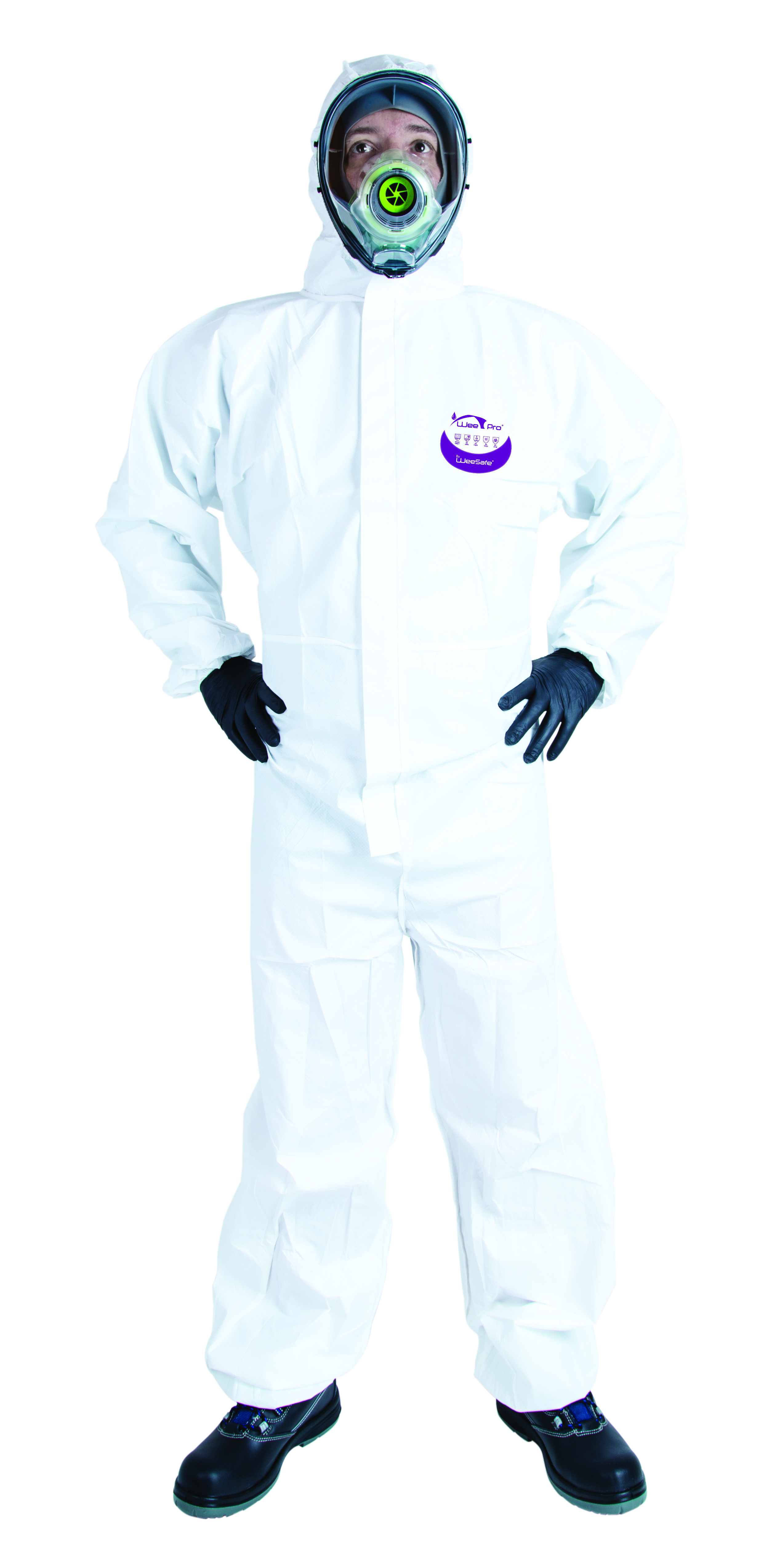
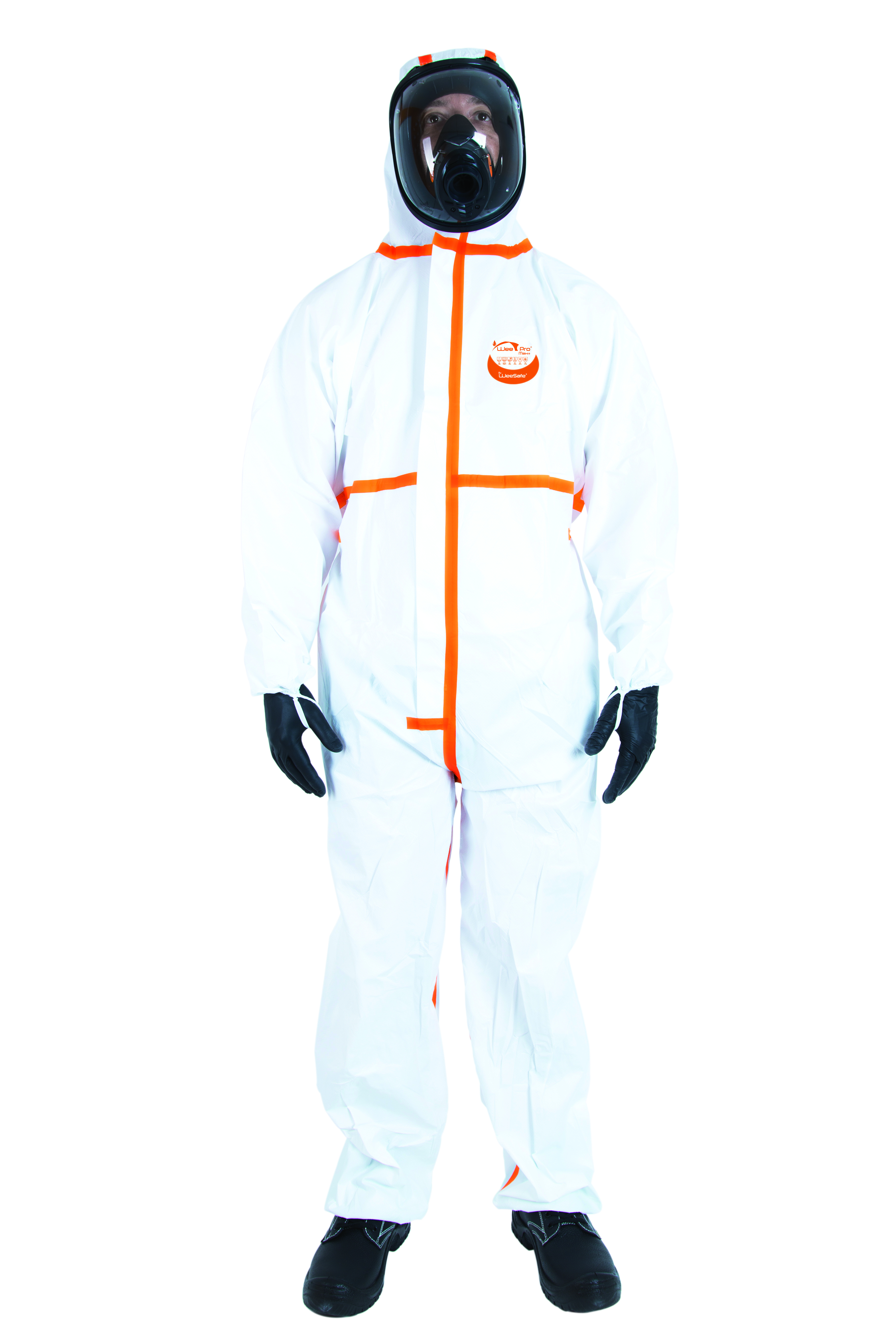
PPE Biological risk
PPE, such as coveralls and gloves, plays a key role in protecting against chemical and biological agents.
Biological agents, present in sectors such as waste reprocessing, wastewater treatment, laboratories, the food industry, and emergency services, expose workers to the risk of serious infections. These agents can be inhaled, ingested, or come into contact with the skin, causing serious, sometimes irreversible, conditions. Simply preventing these risks is often insufficient: personal protective equipment is necessary to ensure worker safety.
Our single-use protective clothing, certified according to EN ISO 14126:2003, achieves the best results against microorganisms in liquid, aerosol or solid particle form, thus guaranteeing maximum safety in hazardous environments.
What are the areas of activity most exposed to biological risks?
Waste treatment
Collection and sorting centers, storage centers, incineration centers, composting (bacteria, mold, enteroviruses).
Water treatment
Sanitation companies, wastewater treatment plants, sewers (salmonella, viruses, bacteria).
Industrial treatment
Vacuum cleaning, disinfection of production areas (mold, yeast, bacteria, fungi).
Agriculture
Mold, microorganisms, prions or NCTAs, activities involving contact with live or dead animals (bacteria, mold, microorganisms, fungi).
Laboratories, epidemics and emergencies
Research laboratory personnel (biology and biotechnology), pharmaceutical industry personnel (vaccine and antibiotic production), medical personnel. In laboratories, wearing clothing that meets standards is mandatory to prevent contamination.
Maintenance and upkeep in industry and construction
Rehabilitation of brownfield sites, maintenance of air conditioning and ventilation systems, maintenance of laboratory automation systems, maintenance of cooling towers, and cleaning companies.
Coveralls
Protective suits are essential for protecting against biological and chemical risks such as microorganisms, aerosols, and contaminated particles in the workplace.
To choose wisely, assess the level of exposure and opt for a suit that complies with the EN 14126 standard, providing protection against infectious agents. Look for sealed seams, an effective barrier against liquids and particles, and a design that promotes comfort and mobility.
Gloves
Gloves are essential protective equipment for protecting against biological agents (viruses, bacteria) during risky handling in the workplace. They protect hands, which are sensitive areas, from infection. Choosing the right gloves requires assessing exposure risks and ensuring they meet standards such as EN ISO 374.
Masks & respirators
Respiratory protection masks are essential for protecting against airborne biological agents, such as particles, aerosols, and microorganisms. They protect the respiratory tract from infection. Choose a mask that meets the risk level (FFP standards according to EN 149), ensuring effective filtration and a good fit.
Goggles
Protective eyewear is essential for preventing biological risks from splashes, droplets, or contaminated particles. It protects the eyes, which are particularly vulnerable, from infectious agents. Choose eyewear that complies with standards (EN 166), offering optimal sealing and a clear field of vision.
Classification of biological agents
Classifying biological agents into four risk levels is essential for assessing hazards and defining appropriate protective measures in exposed environments.
-
Risk Class Level 1: Agents that are harmless to humans and require few preventive measures.
-
Risk Class Level 2: Agents that can cause mild illness but have a low risk of spreading.
-
Risk Class Level 3: Pathogenic agents with a risk of spreading, requiring enhanced protection.
-
Risk Class Level 4: Highly dangerous agents requiring strict protocols to prevent serious contamination.
This system guarantees employee safety based on the pathogenic potential of the chemical and biological agents present. Wearing PPE helps minimize the risks associated with handling various substances.